News
More Than 20 Professional Technicians Service for You
The control of the temperature and humidity environment inside the data center computer room depends on the indoor air conditioning terminal. The computer room air conditioner has the characteristics of high efficiency, high sensible heat ratio, high reliability and flexibility, and can meet the increasing server heat dissipation, humidity constant control, air filtration and other requirements of the data center computer room.
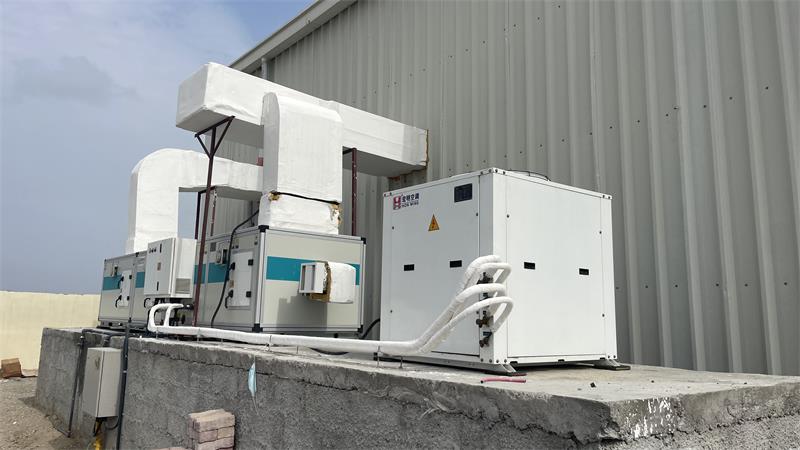

With the stringent requirements of PUE in different regions and the widespread application of high-density servers, new cooling methods in data centers are increasingly being developed and used. The following introduces these traditional and new cooling methods for data centers.
The air-cooled direct evaporative air conditioning system is shown in the figure below. The unit mainly consists of a frame, a compressor, an evaporator, a condenser, an electronic regulating valve, an indoor fan, an outdoor fan, a unit control system, a temperature and humidity sensor, etc. The outdoor fin heat exchanger is used as a condenser, and the indoor fin heat exchanger is used as an evaporator.
The high-temperature gas of the refrigerant discharged by the compressor is condensed into liquid in the outdoor fin heat exchanger, and then throttled and reduced in pressure by the expansion valve to become a low-temperature gas-liquid mixture, and then flows into the indoor fin heat exchanger, absorbs heat and evaporates, and then returns to the compressor to complete a refrigeration cycle; at the same time, the return air from the room is cooled and cooled after passing through the indoor evaporator, and the treated cold air is then sent into the room by the indoor fan.
The low-pressure, low-temperature refrigerant vapor flowing from the evaporator is sucked by the refrigeration compressor, compressed into high-pressure, high-temperature vapor by the compressor and discharged, thus dividing the refrigerant vapor into a high-pressure area and a low-pressure area. The area from the discharge port of the compressor to the inlet of the throttling element is a high-pressure area, and the pressure in this area is called high-pressure pressure or condensing pressure, and the temperature is called condensing temperature.
The area from the outlet of the throttling element to the suction port of the compressor is a low-pressure area, and the pressure in this area is called low-pressure pressure or evaporation pressure, and the temperature is called evaporation temperature. It is because of the pressure difference between the high and low pressures caused by the compressor that the refrigerant flows continuously in the system.
Once the pressure difference between high and low pressure disappears, that is, one of the high and low pressures is balanced, the refrigerant stops flowing. The generation of the pressure difference between the high-pressure area and the low-pressure area and the size of the pressure difference are entirely the result of the compressor compressing the steam. Once the compressor's ability to push the compressed steam, the pressure difference formed is very small, and the refrigeration cycle does not exist. The continuous operation of the compressor is achieved by consuming electrical energy or mechanical energy.
Previous: AIRVent 2025 Exhibition